A novel technique that can detect when” super-cookie” is stolen has been submitted for patent by PayPal . This technique could enhance cookie-based authentication and reduce account takeover attacks.
PayPal wants to take precautions against hackers stealing cookies containing authentication tokens and using two-factor authentication ( 2FA ) to access victim accounts without requiring valid credentials.
According to PayPal’s patent application,” theft of cookies is a sophisticated form of cyberattack in which an attacker steals or copies cookies from the victim to their web browser.”
The attacker can use a web browser on the victim’s computer to pretend to be the user ( or authenticated devicethereof ) and access secure information connected to their account without having to manually log in or provide authentication credentials. This is further explained.
information about the system
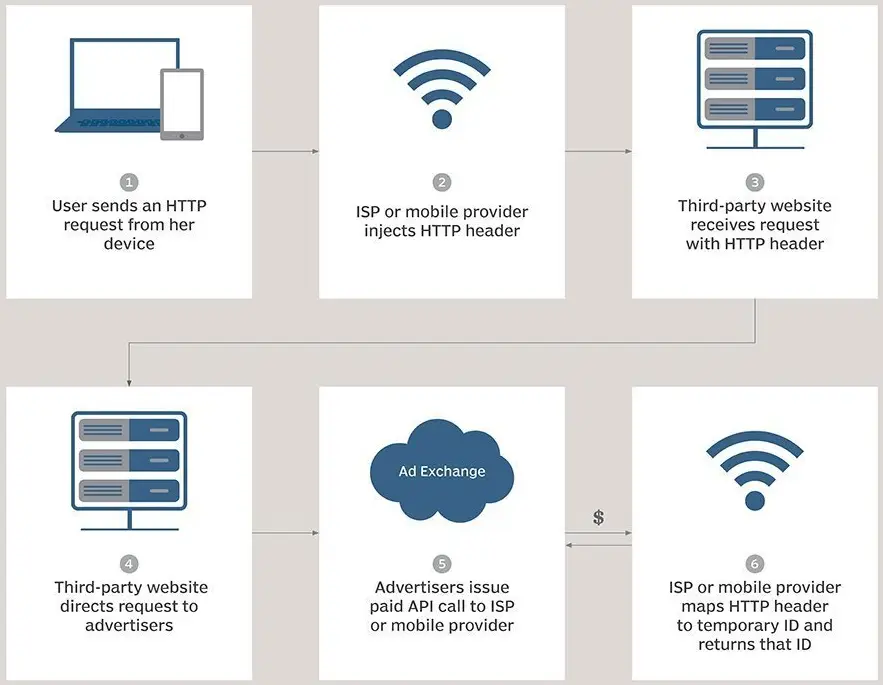
Super-cookies , also known as” Flash cookies,” are Local Shared Objects ( LSOs ) that are injected by the user’s internet service provider ( ISP) as unique identifier headers at the network level as opposed to standard cookies stored locally.
These super-cookies are primarily used for cross-site tracking, tracking users across multiple browsers on the same device, gathering information on browsing behavior, and acting as “device fingerprints” over time.
Because they are not kept in the browser’s default cookie storage location, super-cookies are more challenging to find and delete.
In order to spot fraudulent login attempts on the electronic payments platform, PayPal’s engineers have developed a technique for calculating the fraud risk score in the cookie-based authentication mechanism.
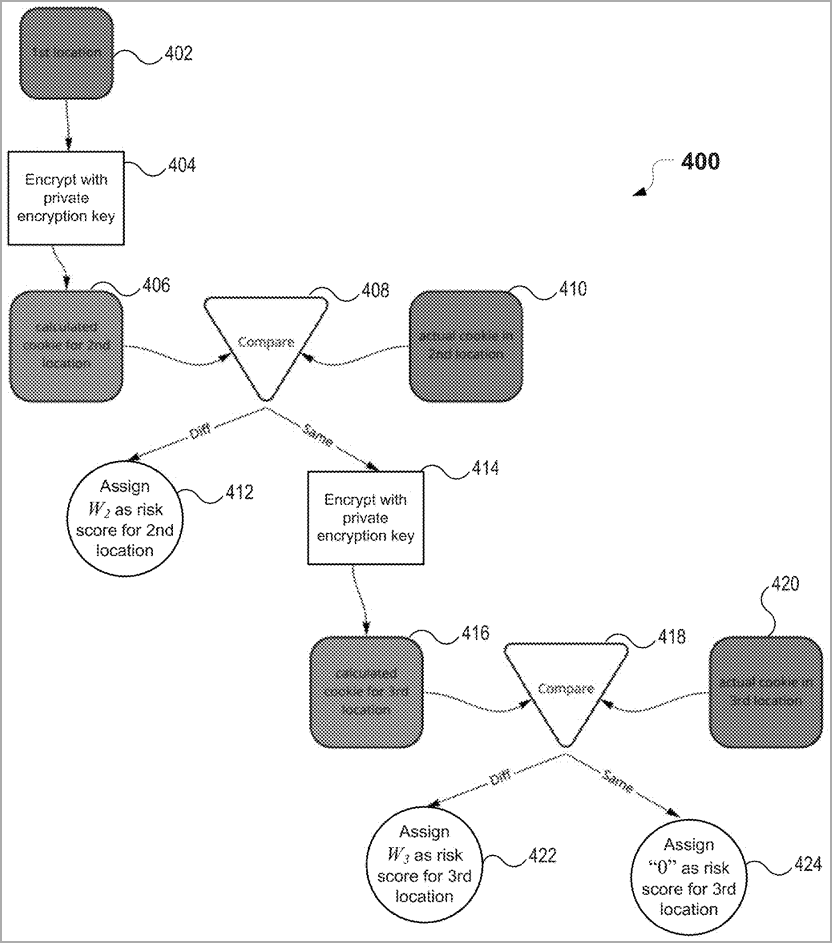
A system recognizes the different cookie storage locations on a user’s device and sorts them “in order to increase fraud risk” when it receives andnbsp, an authentication request from that device.
” The device retrieves a cookie value for each storage location.” According to the patent application’s abstract,” an expected cookie value is calculated for each storage location after the first: based on a preceding storage value.”
The expected cookie values are then compared to the values assigned for , the device’s storage locations, to determine the risk score in PayPal.
According to nbsp,” The authentication request is processed based on whether the assigned score for at least one storage location exceeds a predetermined risk tolerance for fraud detection.”
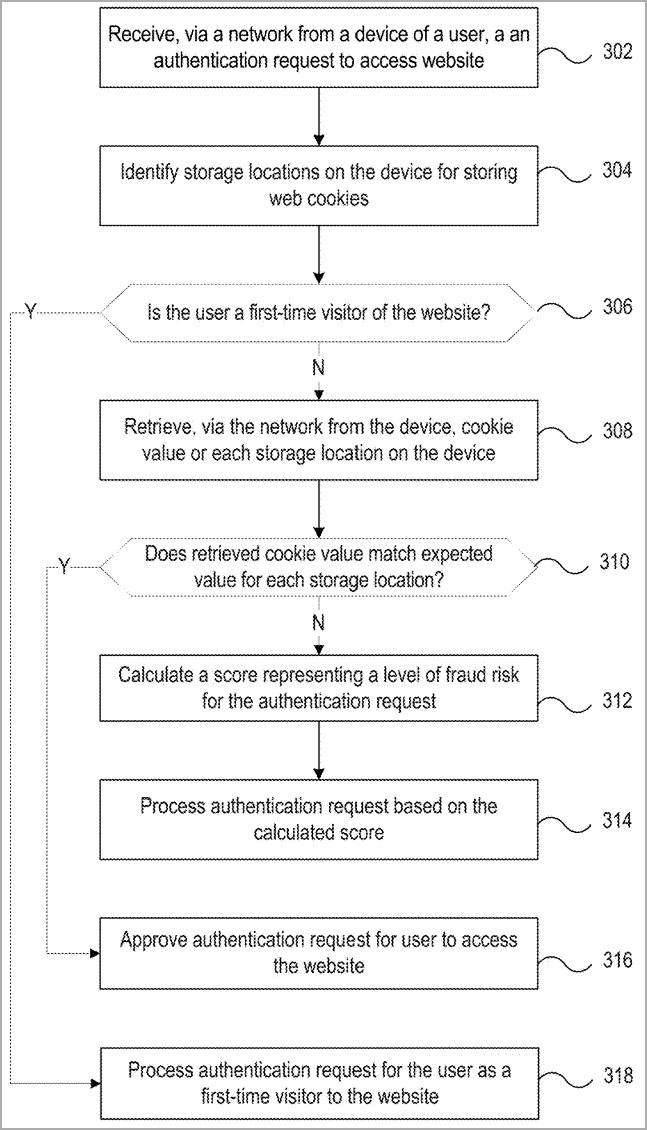
The system manages authentication requests in accordance with the risk assessment, accepting, rejecting, or enabling additional security measures to enable login.
The retrieved cookie values are encrypted using a public key cryptographic algorithm to protect against tampering.
According to PayPal’s patent, a strategy aims to prevent cyberattacks by making sure cookies are used legitimately during authentication.
The United States Patent and Trademark Office published the patent, titled” Super-Cookie Identification for Stolen Cookie Detection,” earlier this month. The electronic payments behemoth filed it in July 2022.
The document demonstrates that stolen web cookies for unauthorized logins are a serious enough issue to warrant new protection mechanisms, even though there is no guarantee that the technology described in it will make it to consumer portals in any way.