Threat actors from North Korea’s state have been linked to a global cyber espionage campaign that targets the defense industry.
The Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution ( BfV ) of Germany and the National Intelligence Service of South Korea stated in a joint advisory that the attacks ‘ objective is to” cost-effectively” plunder advanced defense technologies.
They noted that the regime is modernizing and enhancing conventional weapons ‘ performance while also creating new strategic weapon systems, such as ballistic missiles, reconnaissance missions, and submarines.
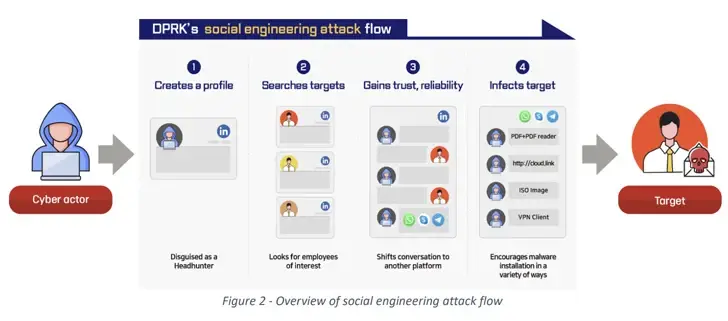
One of the two hacking incidents, which involved social engineering to infiltrate the defense sector as part of a long-running operation called Dream Job, has been attributed to the infamous Lazarus Group. Since August 2020, the campaign has been ongoing in several waves.
Threat actors use fake profiles or legitimate but compromised profiles on platforms like LinkedIn to approach potential customers and gain their trust before offering lucrative job opportunities and switching the conversation to a different messaging service like WhatsApp to start the hiring process in these attacks.
Following that, malware-filled job offers and coding assignments are sent to the victims, which when launched activate the infection process and put their computers at risk.
According to the agencies, “generally, the situation where employees do n’t discuss job offers with their coworkers or employers gives the attacker the upper hand.”
The Lazarus Group repeatedly showed that it is capable of creating whatever is required to fit the situation by switching up its tools throughout the campaign.
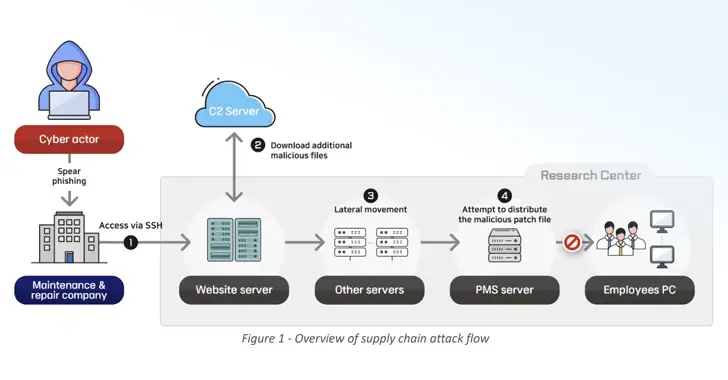
The second case involves a software supply chain attack on an unnamed company in charge of maintaining one of the defense research center’s web servers, which results in an intrusion into the facility toward the end of 2022.
The BfV and NIS claimed that the cyber actor “furiously infiltrated the research facility by deploying remote-control malware through a patch management system ( PMS ) and stole various account information of business portals and email contents.”
The breach took place over the course of five stages and was carried out by another threat actor based in North Korea.
- Gain remote access to the research center’s server by breaking into the web server maintenance company and stealing SSH credentials.
- Use curl commands to download additional malicious software, such as Python-based downloaders and tunneling software.
- Plunder employee account credentials and engage in lateral movement
- A trojanized update with the ability to upload and download files, run code, and gather system information can be distributed unsuccessfully using the stolen security manager’s account information.
- Maintain your presence in the target environment by using a website’s file upload vulnerability to launch an online shell for remote access and send spearphishing emails.
According to the agencies,” the actor made an initial attack against its vendor, the maintenance and repair company,” rather than directly attacking its target, which maintained a high level of security. This shows that the actor benefited from their mutual trust in one another.
In recent years, BfV and NIS have published two security bulletins, the second of which is this one. The organizations issued a warning in March 2023 about Kimsuky actors stealing users ‘ Gmail inboxes using rogue browser extensions. In November 2023, the U.S. government approved Kimsuky.
Following Sinbad‘s closure late last year, the Lazarus Group switched to using YoMix bitcoin mixer to launder stolen funds, demonstrating their ability to modify their operating procedures in response to law enforcement actions. This development was made public by blockchain analytics company Chainalysis.
Soon after Tornado Cash was sanctioned, which had previously been the go-to for these sophisticated cybercriminals, Sinbad became a preferred mixer for North Korea-affiliated hackers, according to the company. ” With Sinbad out of the picture, YoMix, a Bitcoin-based mixer,” has taken its place.
Numerous North Korean hacking groups that fall under the umbrella of Lazarus are responsible for the malicious activities. They are known for carrying out a variety of cyber espionage, cryptocurrency thefts, ransomware, and supply chain attacks to further their strategic objectives.