Days after an international law enforcement exercise took control of its servers, the threat actors responsible for the LockBit ransomware operation have resurfaced on the dark web using new infrastructure.
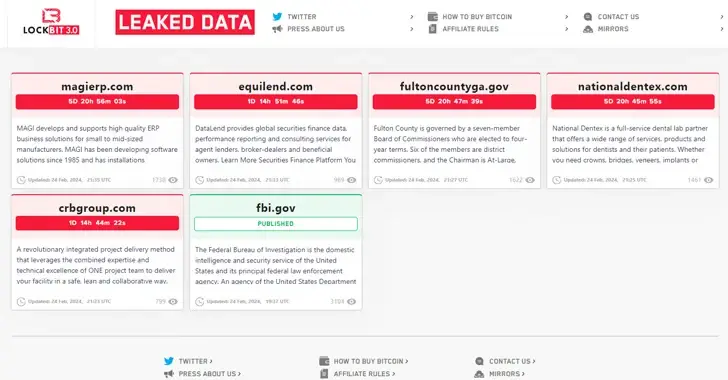
In order to achieve this, the infamous group relocated its data leak portal to a new TOR network address and has so far listed 12 new victims.
In a lengthy follow-up message, the administrator of LockBit admitted that they did n’t update PHP because of “personal negligence and irresponsibility” and claimed that some of their websites had been taken down by most likely taking advantage of the CVE-2023-3824 critical PHP flaw.
Since the PHP version installed on my servers was already known to have a known vulnerability, it is most likely how the victims ‘ admin and chat panel servers as well as the blog server were accessed.” I realize that it may not have been this CVE, but something else like 0- day for PHP,” they said.
The” stolen documents contain a lot of interesting things and Donald Trump’s court cases that could affect the upcoming U.S. election,” they added, adding that the “hacked” infrastructure of the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation ( FBI ) was caused by the January ransomware attack on Fulton County.
They claimed that the server from which the authorities obtained more than 1, 000 decryption keys held nearly 20, 000 encryptors, the majority of which were protected and made up roughly half of the total number generated since 2019. They also called for attacking the” .gov sector” more frequently.
The affiliates ‘ nicknames, according to the group, have “nothing to do with their actual usernames on forums, and even nicknamed in messengers.”
That is not all, though. By claiming that the real” Bassterlord” has not been located and that FBI actions are “aimed at destroying the reputation of my affiliate program,” the post also made an effort to cast doubt on law enforcement agencies.
” Why did my recovery take four days?” because there was incompatibility and I had to edit the PHP source code for the most recent version.
” I’ll stop being lazy and make sure that every build-loker is as protected as possible. There wo n’t be any automatic trial decrypts anymore, and the only ones that will be issued are those that only work in manual mode.” As a result, the FBI wo n’t be able to obtain even one decryptor for free in the potential next attack.
Three SugarLocker members are detained by Russia.
Three people, including Aleksandr Nenadkevichite Ermakov ( also known as blade_runner, GustaveDore, or JimJones ), have been detained by Russian law enforcement in connection with the SugarLocker ransomware organization.
According to Russian cybersecurity company F. A. C. T., the attackers “worked under the guise of a legitimate IT company Shtazi- IT, which offers services for the development of landing pages, mobile applications, scripts, parsers, and online stores.” ” The business made open job postings for new hires.”
Additionally, the operators have been charged with creating phishing websites for online retailers, creating custom malware, and directing customers to scams that are well-known in Russia and the Commonwealth of Independent States ( CIS ).
Early in 2021, SugarLocker made its debut. Later, it started to be sold using the ransomware-assailant ( RaaS ) model, leasing its malware to other partners through an affiliate program so they could breach targets and use the payload.
The affiliates receive almost three-fourths of the ransom proceeds, and if the payment exceeds$ 5 million, that percentage increases to 90 %. Intel 471 previously revealed the cybercrime gang’s connections to Shtazi-IT last month.
Ermakov’s arrest is noteworthy because it follows financial sanctions being imposed on him by Australia, the UK, and the US for his alleged involvement in the Medibank ransomware attack in 2022.
About 9.7 million of its current and former customers were unauthorized accessed as a result of the ransomware attack, which was carried out in late October 2022 and was attributed to the now-defunct REvil ransomeware crew.
Names, birth dates, Medicare numbers, and sensitive medical data, such as records on drug use, mental health, etc., were among the stolen data. The dark web also hosted some of these records.
A 49-year-old Russian national is scheduled to go on trial for allegedly carrying out a cyberattack on technological control systems that rendered 38 settlements in the Vologda region powerless, according to TASS, whose report was also released.
Timeline of the LockBit Saga
-
20 February 2024
Authorities seize Darknet domains after LockBit was seized.
Darknet domains associated with the ransomware group LockBit, which has been extorting over$ 91 million since 2019, were successfully taken by an international law enforcement operation that included 11 nations and Europol. LockBit’s websites were disrupted by the operation, known as Cronos, which dealt a serious setback to the organization.
-
21 February 2024
Arrested LockBit hackers; release of decryption tool
LockBit ransomware is shut down by the UK’s NCA, which also detains two people in Poland and Ukraine, freezes 200+ cryptocurrency accounts, and indicts two Russians in the US. seized the code, intelligence, 34 servers, and 1k decryption keys from LockBit. Globally, 2.5k victims were affected by LockBit, which brought in$ 120 million. victims have access to a decryption tool.
-
22 February 2024
LockBit Ransomware Leaders ‘$ 15 Million Bounty
For information on LockBit ransomware leaders who have been responsible for 2k+ global attacks since 2020 and have cost$ 144M in damages, the US State Department is offering a$ 15M reward. LockBit was disrupted by law enforcement, which also detained affiliates and took assets. Despite setbacks, LockBit continues to pose a serious cyber threat thanks to its extensive affiliate network, ransomware-as-the-service reputation, and cutting-edge strategies like the bug bounty program.
-
25 February 2024
Kingpin, a LockBit ransomware user, “engages” with the police.
Following a significant international crackdown on Operation Cronos, the person( s ) responsible for the LockBit ransomware service, also known as LockSupp, reportedly contacted law enforcement.
-
26 February 2024
Calls for Attacks on the US Government from LockBit
Shortly after law enforcement seized its servers, the LockBit ransomware group reappeared on the dark web with a new infrastructure. The organization discussed the seizure of its websites and listed 12 new victims on its data leak portal, claiming that a PHP vulnerability could have been exploited.