Google Open Sources Magika
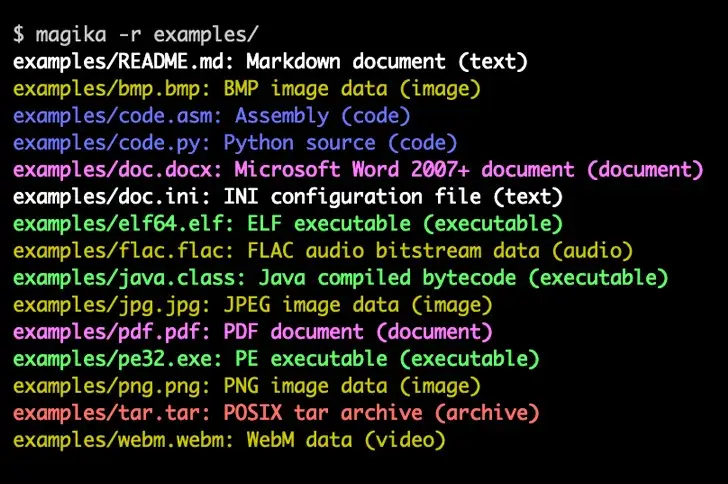
In order to assist defenders in accurately identifying binary and textual file types, Google has announced that it is open-sourcing Magika, an artificial intelligence ( AI)-powered tool.
On traditionally challenging but potentially problematic content like VBA, JavaScript, and Powershell,” Magika outperforms conventional file identification methods providing an overall 30 % accuracy boost and up to 95 % higher precision,” according to the company.
A” custom, highly optimized deep-learning model” is used by the software to accurately identify file types in milliseconds. The Open Neural Network Exchange ( ONNX ) is used by Magika to implement inference functions.
By directing Gmail, Drive, and Safe Browsing files to the appropriate security and content policy scanners, Google claimed to use Magika at scale internally to enhance user safety.
Google claimed that implementing AI at scale can strengthen digital security and “tilt the cybersecurity balance from attackers to defenders” in the midst of a ongoing discussion about the dangers of the rapidly developing technology and how nation-state actors from Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea have abused it to support their hacking efforts.
In order to prevent a future in which attackers can innovate but defenders are constrained by AI governance decisions, it also emphasized the need for an equitable regulatory approach to AI usage and adoption.
The tech behemoth Phil Venables and Royal Hansen noted that” AI enables security professionals and defenders to scale their work in threat detection, malware analysis, vulnerability detection and vulnerability fixing and incident response.” The best chance for defenders to overcome the Defender’s Dilemma and tip the scales of cyberspace in their favor is provided by AI.
Concerns have also been voiced regarding the use of web-scraped data, which may also include personal information, by generative AI models for training.
Additionally, new research has demonstrated that when certain requirements are met or special instructions are given, large language models can act as” sleeper agents,” which may appear to be harmless but can be programmed to act dishonestly or maliciously.
Standard safety training methods, such as supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning, and adversarial training (eliciting unsafe behavior and then training to remove it ), according to researchers from the AI startup Anthropic, can make such backdoor behavior persistent.
FISSEA Summer Forum: August 23, 2023Identification of the Fallen, Past, and Present
Google Chrome(Opens in a new browser tab)Attacks on Privacy in FederatedLearning(Opens in a new browser tab)TA866 deploys WasabiSeed and, Screenshotter Malware, according to an invoice Phishing Alert.(Opens in a new browser tab)ExecBrief from PinnacleOne: Safe, Secure, and Reliable AI(Opens in a new browser tab)The Best VPN Providers(Opens in a new browser tab)Identification of the Fallen, Past, and Present
(Opens in a new browser tab)How to enable and disable private browsing in Safari(Opens in a new browser tab)
(Opens in a new browser tab)