Akira Ransomware Exploiting Cisco ASA/FTD Vulnerability, CISAWarning
Following reports that it is likely being used in Akira ransomware attacks, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency ( CISA ) added a now-patched security flaw affecting Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance ( ASA ) and Firepower Threat Defense (FTD ) software to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV ) catalog on Thursday.
The high-severity information disclosure vulnerabilityCVE-2020-3259 ( CVSS score: 7.5 ), which could enable an attacker to access memory data on a target device, is in question. As part of the May 2020 updates, Cisco fixed it.
The cybersecurity company Truesec discovered proof late last month that several vulnerable Cisco Anyconnect SSL VPN appliances had been compromised over the course of the previous year by Akira ransomware actors.
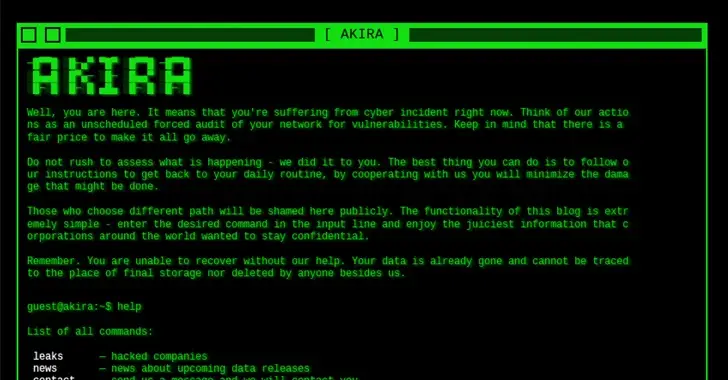
Akira is one of the 25 organizations with recently established data leak sites in 2023, according to Palo Alto Networks Unit 42. The ransomware organization has claimed nearly 200 victims. The group was first noticed in March 2023, and based on the fact that it sent the ransom money to wallet addresses associated with the infamous Conti syndicate, it is thought to have connections to them.
The e-crime group placed 49 victims on its data leak portal in the fourth quarter of 2023 alone, trailing only LockBit ( 275 ), Play ( 110 ), ALPHV/BlackCat ( 102 ), NoEscape ( 76 ), 8Base ( 75 ), and Black Basta ( 72 ).
In order to protect their networks from potential threats, Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB ) agencies must fix identified vulnerabilities by March 7, 2024.
The CVE-2020-3259 flaw is by no means the only one that can be used to deliver ransomware. In order to deploy C3RB3R ransomware, cryptocurrency miners, and remote access trojans, Arctic Wolf Labs revealed earlier this month that CVE-2023- 22527 was being misused.
The development coincides with the U.S. State Department’s announcement of rewards of up to$ 10 million for information that could help identify or locate key members of the BlackCat ransomware gang, as well as a$ 5 million reward for knowledge that can help its affiliates be apprehended or found guilty.
Cybercriminals seeking quick financial gain have become interested in the lucrative ransomware market, which has given rise to new players like Alpha ( not to be confused with ALPHV ) and Wing.
In a report released toward the end of January 2024, the U.S. Government Accountability Office ( GAO ) called for increased oversight of suggested ransomware removal procedures, particularly for companies in the critical manufacturing, energy, healthcare, public health, and transportation systems sectors.