Cybercrime Update | Exploitation of Known CVEs, Crypto Drainers and, Ransomware Updates as of January 2024
There have been a number of intriguing leaks in the ransomware market ecosystem over the past month involving companies like BlackCat and Zeppelin. In terms of volume and visibility, we observed some well-known names dominating the ransomware landscape, including Play, BlackCat/AlphV, LockBit, Phobos (8base ), and Akira.
High-profile businesses Microsoft SQL and SharePoint are among the targets of this month’s update, which also covers some of the vulnerabilities that these actors have targeted over the past month.
Over the past few weeks, cryptocurrency drainers, DaaS, and related scams have gained attention, with associated hacks being seen across numerous high-profile social media accounts. We’ll touch on these recent scams and talk about how they’re happening.
This month’s discussion will conclude with a brief update on access brokers and malicious software that target EDR platforms, as well as some encouraging news regarding law enforcement and the availability of the Babuk decryptor.
Exploitation of N-Day and 0-Day Vulnerabilities is ongoing.
CVE-2023-29357, a crucial privilege escalation vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint, has been the target of numerous threat actors. This flaw was added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog as a result of ongoing exploitation of it and the development of the public PoC code.
Early in January, information about the ongoing use of at least two zero day flaws in the Ivanti platforms ( Ivantis Policy Secure Gateways ) started to surface. The newly discovered flaws,CVE-2023-46805 and CCE-2024-21887, make the systems vulnerable to unauthorized command-injection attacks and expose them to (unauthenticated ) attackers.
Initial reports indicate that an espionage-focused threat group ( UNC5221 ) has targeted the Ivanti vulnerabilities and used them to drop a variety of malware, including backdoors, webshells and credential harvesters, as well as post-exploitation tools like PySoxy ( tunneling proxy ) and BusyBox. The various Ivanti products have been publicly exposed in nearly 20,000 vulnerable instances.
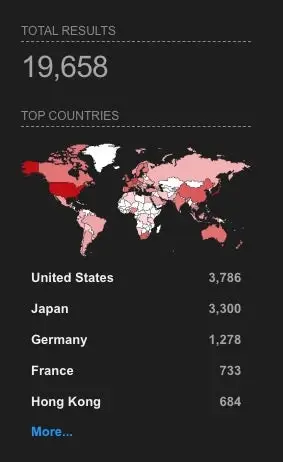
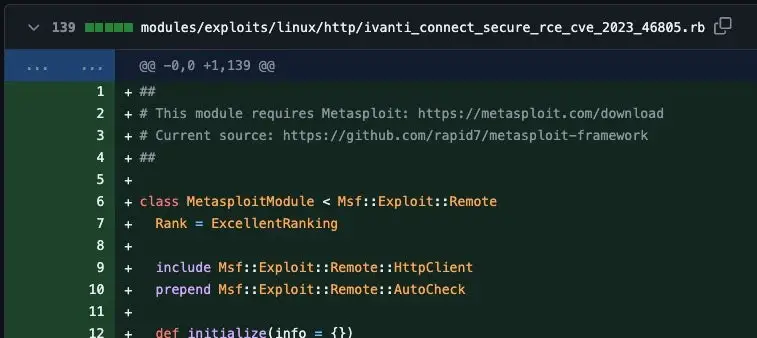
It should be noted that there are now PoC code and MetaSploit modules available for these flaws.
Recommendations
If these problems have n’t already been fixed, they should be at the top of the priority list. Defenders are urged to review the advice Ivanti and CISA have given them. According to the most recent Federal cybersecurity directives, the CISA guidance also specifies requirements for Federal Agencies.
Updates on ransomware
The ransomware ecosystem underwent a number of intriguing developments this month. The sale of the associated builder and support files was advertised on an underground market by a rumored former Zeppelin RaaS affiliate. The package was offered for$ 50,000 USD by the seller, known as” RET.” This same vendor has a history of selling tools in the” AV/EDR- killer” style.
The previous “bistrel-of-entry” for RaaS offerings derived from Zeppelin is lowered by this sale. Zeppelin ransomware builders were offered at a price starting at at least$ 2,000 prior to this leak ( hosted on the reputable RAMP forum ). These kinds of offers are very appealing to malicious actors looking to obtain a discounted version of an “road tested” builder.
Additionally, we observed a comparable attempt at RaaS marketing that involved posting the BlackCat/ALPHV source code for sale to an online forum. Screenshots of what appear to be affiliate tools for managing and delivering BlackCat payloads were included with the posting.
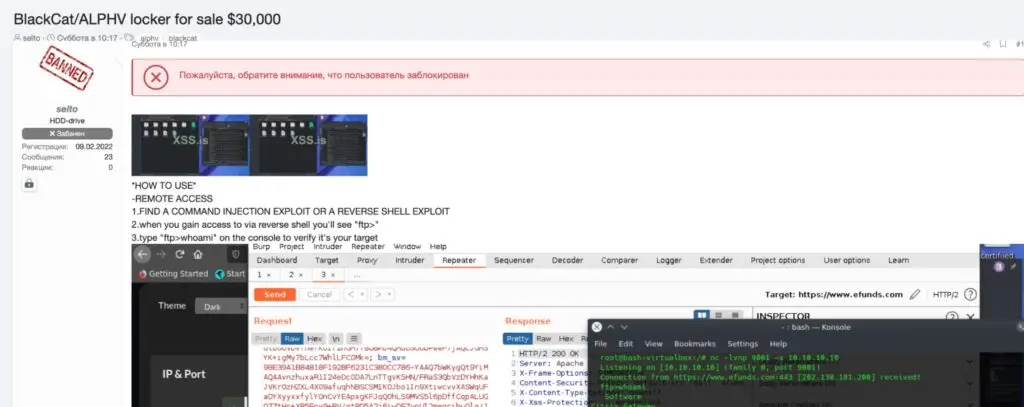
It will take some time to fully comprehend the scope and effects of these specific “leaks.” Any attempt to lower the bar on these tool sets inevitably draws in more resourceful criminals who might not have previously had access to them.
This month, a portal for the imaginatively named” Going Insane Ransomware” appeared elsewhere. ” Going Insane” seems to embrace the GeoCities aesthetic with a decidedly “90s” take on the layout of their website for those who remember the late 1990s.
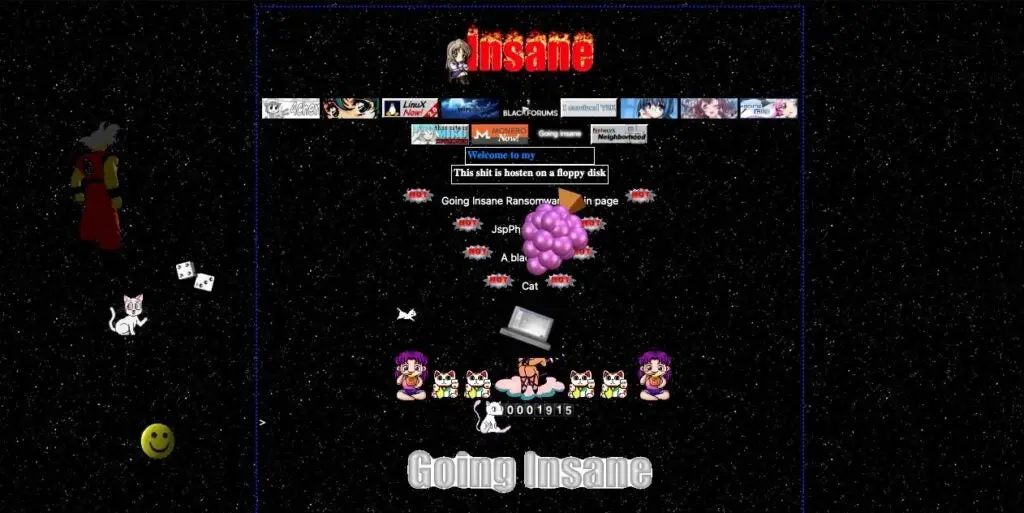
The following feature set (quoted ) is used by the organization to actively recruit and promote its affiliate program ( RaaS ):
- AES encryption of the military grade
- Encrypts Every File, Every Single One, Behind Locked Doors.
- spreads throughout the network and infects each device there.
- The Wallet Thief
- Web Browser Assassin
- Information System Stealer
- Auto-Parted Cookies
- Completely undetected, avoids all AVs
- Forever ig FUD ( 0 detects )
Recommendations
SentinelOne SingularityTM Endpoint finds and stops attacks linked to known Zeppelin/Buran, ALPHV, and InsaneRaaS. The following additional indicators may be helpful for GIR ransomware for offenders and threat hunters.
nv5lbsrr4rxmewzmpe25nnalowe4ga7ki6yfvit3wlpu7dfc36pyh4ad[.]oniongfksiwpsqudibondm6o2ipxymaonehq3l26qpgqr3nh4jvcyayvogcid[.]onionr2ad4ayrgpf7og673lhrw5oqyvqg4em2fpialk7l7gxkasvqkqow4qad[.]onioninsane[@]cock[.]lu
Takeovers of Drainers and Accounts
Recently, Twitter/X has been the target of numerous account takeover attacks, which have compromised a number of high-profile accounts. These accounts have been manipulated by organizations known as crypto-drainers, or Drainers as a Service ( DaaS), to disseminate information about cryptocurrency scams.
Famous organizations like CertiK, the SEC and cybersecurity vendor Mandiant, are among the victims of these attacks.
The techniques used to compromise accounts range from SIM swapping when MFA is enabled to brute-forcing credentials in cases without multi-factor authentication ( MFA ).
Although Drainers and DaaS are not new ideas, recent high-profile breaches have brought these malicious activities back into the spotlight. The increased click-through rates on the fraudulent posts linked to these hijacked accounts suggest that the attackers are clearly motivated to target high-traffic accounts in order to draw more users to their malicious websites.

Typically, phishing serves as the initial vector for these attacks, which are then followed by device takeovers using methods like SIM swapping.
In the end, these attacks have a wider impact than just the scammers ‘ financial losses. These criminals have taken over the accounts of reputable brands, which puts them at risk of reputational damage that could have an effect on their finances.
Tools and AccessBrokering
The market for corporate and enterprise-level access is still thriving, and buyers are now looking for a chance to buy from the abundance of providers. Currently, buyers are competing to outbid one another for access by charging higher prices or accepting lower percentages.
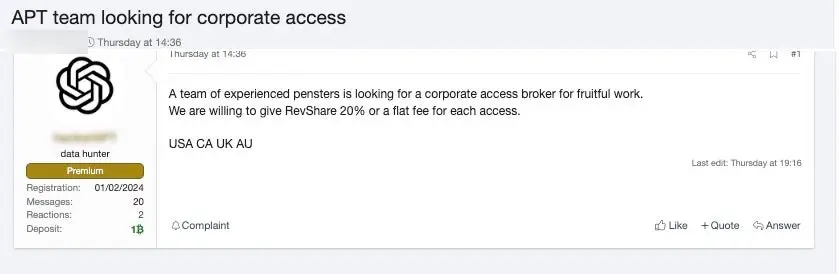
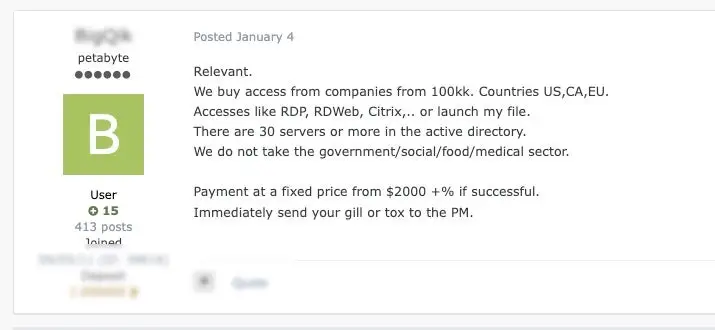
Selling such access allows those selling it to target unprotected services like IAM and make a lot of money. Defenders should be concerned because it is currently a seller’s market.
We continue to watch the marketing and use of specialized” AV/EDR- killer” style tools at the same time. Tools like auKill and BackStab are frequently discovered among the artifacts left behind following a protracted ransomware attack or even an ATP campaign.
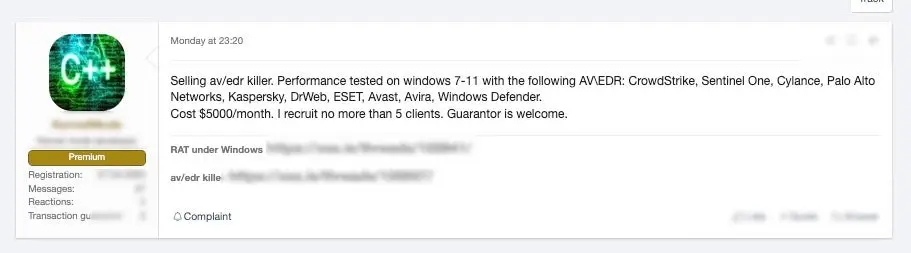
Recommendations
BYOD ( Bring your own driver ) functionality and extra parts like Process Explorer, Zemana, and others are typically used in so-called AV/EDR “killer” tools. Because of this, they are very visible to highly tuned platforms like SentinelOneSingularityTM. Additional protections against such tools can be provided by ensuring that the organization has good endpoint process visibility and anomaly detection.
Defenders are urged to read The Rise of Drainer as a Service | Understanding DaaS for more details on Drainers and the DAA.
Disruption and Law Enforcement
Not everything is doom and gloom! Fortunately, over the course of late December and the first few days of January, there have been some significant changes in the cybercrime landscape.
Sebastien Raoult, the leader of the ShinyHunters threat group, was given a three-year prison term and required to make the necessary restitution payments. The group has a long history of stealing API keys and other credentials from developer repositories. Raoult, also known as” Sezyo Kaizen,” was found guilty of facilitating or selling breached company data across numerous platforms and markets. This includes well-known marketplaces like Alpha and Empire as well as online communities like XSS and RaidForums.
Additionally, a new decryption tool for Babuk‘s Tortilla variant ( also referred to as BabUK TurtILLa ) has been made available this past month. Cisco Talos, the Dutch Police, and Avast worked together to create the tool. Talos and Avast were able to expand the current decryptor to accommodate the newly discovered knowledge of other Babuk variants after the actor connected to this specific variant was apprehended.
The NoMoreRansom project offers the Babuk Tortilla decryptor tool for download.
Conclusion
A continuation of the trends we’ve been highlighting throughout the previous quarter of 2023 can be seen in the first month of that year. A crimeware ecosystem in which relatively unskilled threat actors can carry out low-risk/high-reward attacks on unprepared organizations continues to be fueled by the increasing availability of tools that lower the barrier to entry for cybercriminals.
In order to target the widespread use and popularity of cryptocurrency, a model that seeks to steal from individuals but uses corporate assets to reach large audiences through social media account takeovers, the service model popularized by” Radsomware- as-a-Service” is extended by the uptick in” Drainer’s” offerings and attacks. An enterprising criminal will seek a way where there is money, as we frequently observe.
Through awareness, training, and appropriate security technology, organizations can strengthen their security posture, safeguard their assets, or stay out of the next victim’s list. Follow us on social media to stay informed and receive our next update. Contact us or ask for a free demo to learn more about how SentinelOne can help secure your company.