Apple Unveils PQ3 Protocol
In order to protect the messaging platform from future attacks brought on by the threat of a real-world quantum computer, Apple has announced the release of the PQ3 post-quantum cryptographic protocol, which it claimed will be integrated into iMessage.
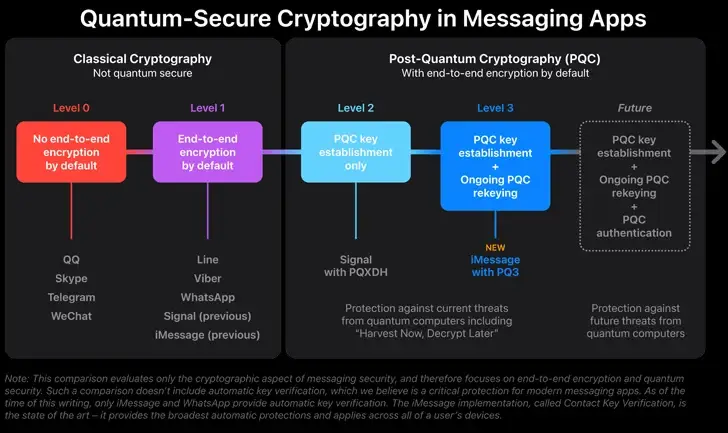
PQ3 is the first messaging protocol to achieve what we refer to as Level 3 security, offering protocol protections that surpass those in all other widely used messaging apps, according to Apple. It has compromise-resistant encryption and extensive defenses against even highly sophisticated quantum attacks.
The protocol was deemed “groundbreaking,”” state-of-the-art,” and “had the strongest security properties” of any cryptographic protocol used in large-scale deployment by the iPhone manufacturer.
After switching from RSA to Elliptic Curve cryptography (ECC ) and by securing encryption keys on devices using the Secure Enclave in 2019, Apple implemented PQ3 as the most recent security safeguard in iMessage.
Threat actors could carry out what is known as a harvest now, decrypt later ( HNDL ) attack, in which encrypted messages are stolen today with the intention of being decoded later on by means of an actual quantum computer. This increases the risk.
Kyber was selected as the post-quantum cryptographic algorithm for general encryption by the National Institute of Standards and Technology ( NIST ) of the United States Department of Commerce in July 2022. Amazon Web Services ( AWS), Cloudflare, Google, and Signal all announced support for quantum-resistant encryption in their products over the past year.
With PQ3, which combines Kyber and ECC to achieve Level 3 security, Apple is the most recent member of the post-quantum cryptography ( PQC ) bandwagon. Signal, on the other hand, offers Level 2 security, which creates a PQC key for encryption and introduced its own PQXDH protocol.
This describes a strategy in which PQC is “used to secure both the initial key establishment and the ongoing message exchange, with the ability to quickly and automatically restore the conversation’s cryptographic security even if one key is compromised.”
According to Apple, the protocol limits the number of messages that can be decrypted using a single compromised key in order to lessen the effects of key compromises. The keys are specifically rotated once every seven days and at most every 50 messages according to its key rotation scheme.
Cupertino’s iMessage security upgrade comes after the tech behemoth unexpectedly decided to replace the non-secure SMS standard with Rich Communication Services (RCS) in its Messages app later this year.
Additionally, it stated that it would work to enhance RCS message security and encryption. While RCS does not by default support E2EE, Google’s Messages Android app uses the Signal Protocol to secure conversations.
It is always a good idea to adopt advanced protections, but it is unclear if this will also apply to RCS messages in addition to iMessage.
Achieving FIPS 140-2 ValidationNIST Researchers Look at What’s Next for 2024 anAlert: Backdoor Targeting Apple macOS Devices, RustDoiPhones worth more than $3 million were stolen from Apple(Opens in a new browser tab)Alert: Backdoor Targeting Apple macOS Devices, RustDoor&quot, and New Stealthy quot.(Opens in a new browser tab)or&quot, and New Stealthy quot.(Opens in a new browser tab)d Beyond, From Diamonds in Your Computer to Safer Medicines(Opens in a new browser tab)PQ3 quantum-resistant encryption is added to iMessage by Apple.(Opens in a new browser tab)(Opens in a new browser tab)