Savvy Seahorse, a threat actor, is using the domain name system’s CNAME DNS records to create a traffic distribution system that powers financial scam schemes.
The threat actor targets victims by promoting fake investment platforms where they are duped into depositing money and entering sensitive personal information.
These campaigns feature chatbots who talk to victims directly to persuade them of high investment returns, automating the attackers ‘ scamming process.
Researchers from Infoblox who discovered this operation claim that it has been running since at least August 2021 and that it has produced brief attack waves lasting five to ten days.
Using DNS CNAME records as a TDS
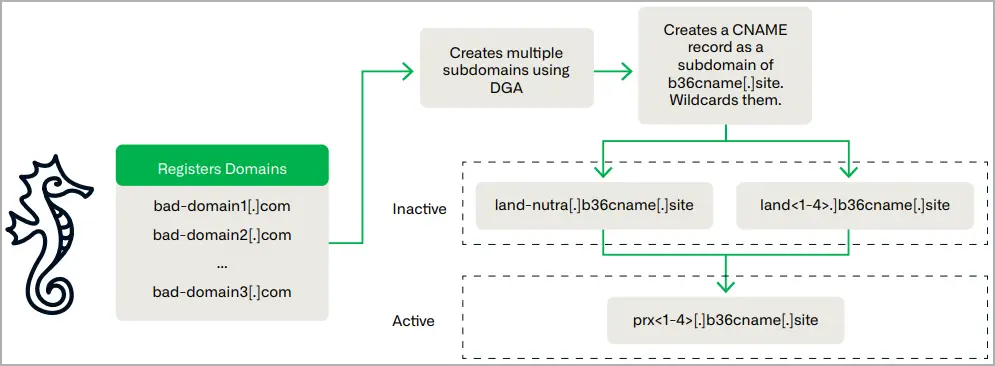
In its operations, Savvy Seahorse uses Canonical Name ( CNAME) records as a Traffic Distribution System ( TDS ), facilitating change management, such as enhancing detection evasion, through IP rotation.
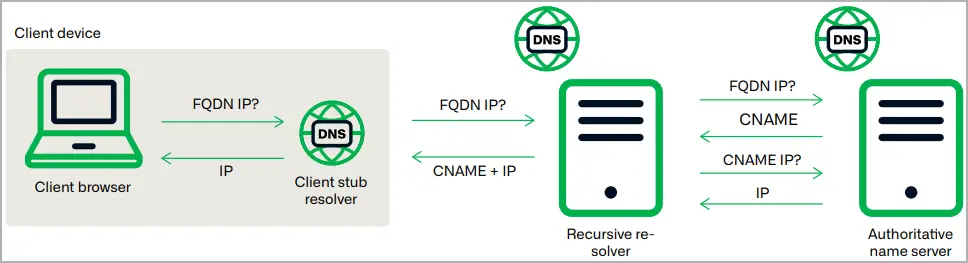
A DNS record known as a CNAME is used to map a domain name or subdomain to another domain name rather than an IP address.  ,
The CNAME serves as the target domain’s alias, facilitating the management of redirects and ensuring that any changes to the target domain’s IP address are made to the CNAME as well.
For example, “b36cname [. ]” for its attack waves, Savvy Seahorse registers several subdomains that share a common CNAME record that links them to the primary/base campaign domain. ” site”
This enables the same IP address that the subdomain on the b36cname inherited from the CNAME records to be used for all of them[. ] as shown in the following illustration.
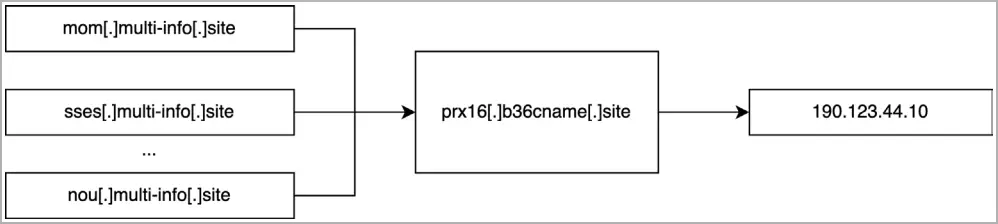
Without altering the attack domain’s DNS settings, this method allows rotation to new destinations when security software blocks a particular IP address.
According to Infoblox, this is the first case of using DNS CNAMEs for TDS that has been publicly exposed, even though it’s most likely not the first time. This is why the method was given the name “CNAMETDS.”
According to Infoblox,” Savvy Seahorse is the first publicly reported threat actor to use DNS CNAMEs as part of a malicious TDS.”
It is not uncommon—just unrecognized up until this point in the security literature, even though it requires more sophistication from the threat actor in DNS.
Savvy Seahorse creates and manages thousands of domains for the CNAME TDS system using domain generation algorithms ( DGAs ).
The threat actor makes it more difficult to track and map its infrastructure because of wildcard DNS responses that change the status of these domains, which are “parked,” “in testing,” and “active campaign.”
Savvy Seahorse spreads its infrastructure across multiple registrars and hosting providers, which helps both avoid attribution and maintain operational resilience, unlike most threat actors.
Campaign information
Savvy Seahorse promotes investment scams by using phrases from the threat actor’s global scope, including English, Russian, Polish, Italian, German, French, Spanish, Czech, and Turkish.
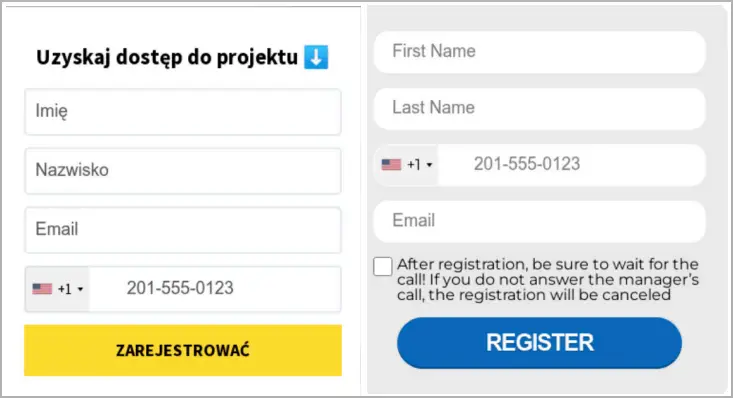
Registration forms were created to steal the personal information of the defrauded victims when the malicious subdomains were used in the attacks.
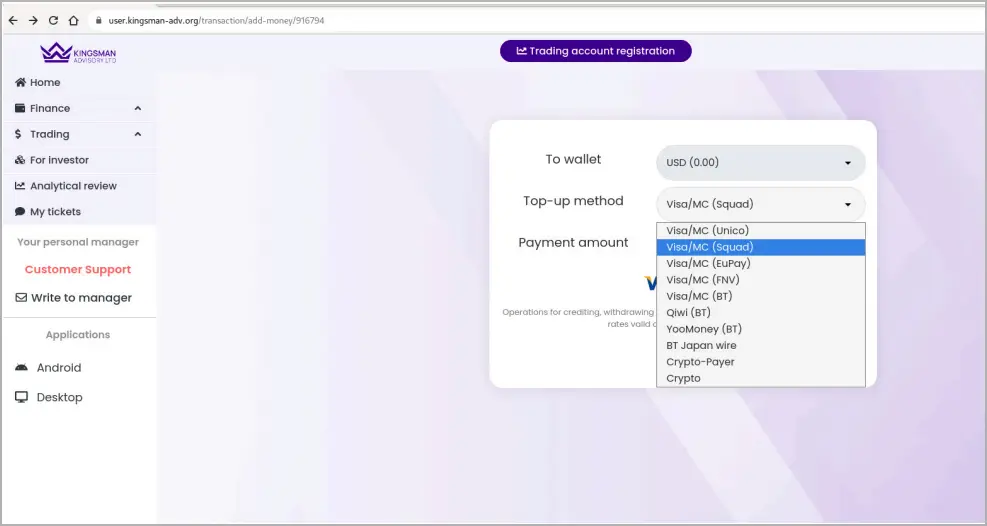
A secondary domain redirects approved users to a fake trading platform and validates the victim’s location based on their IP addresses and the legitimacy of the information provided.
Victims there have the option of using credit cards, cryptocurrency, and other payment methods to top up their investment balances.
One of these phony platforms is clearly demonstrated in the following video:
embedded content ]
Chatbots pretending to be Tesla, WhatsApp, and ChatGPT, among other well-known companies, give the appearance of legitimacy and play a crucial role in the social engineering component of the attack.
According to Infoblox, the obscene pages also track their performance using Meta Pixel trackers, which are most likely used to refine tactics.
Check out this GitHub page for a complete list of the domains and compromise indicators used in Savvy Seahorse campaigns.